Graphics
DOI-assigned graphical abstracts created & published by PubDraw.
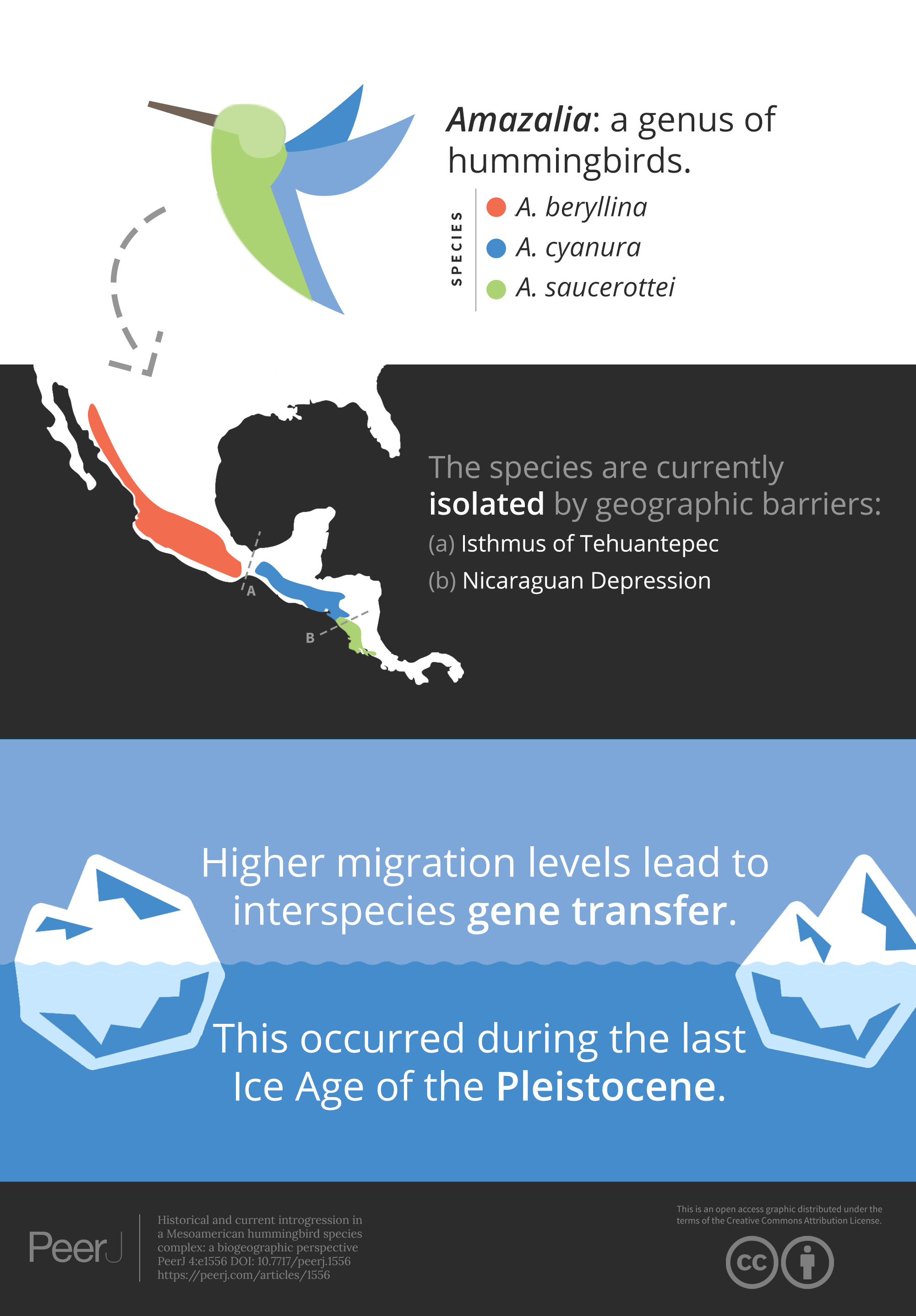
Geographic barriers determine hummingbird species distribution
Glacial cycles during the last Ice Age induced changes in the distribution of species. When distribution ranges expand, closely related species might get in contact and interbreed. By documenting higher historical levels of migration of the nuclear genome between species compared to contemporary levels, researchers suggest that current genetic structure resulted form limited dispersal across the isthmus and depression barriers.
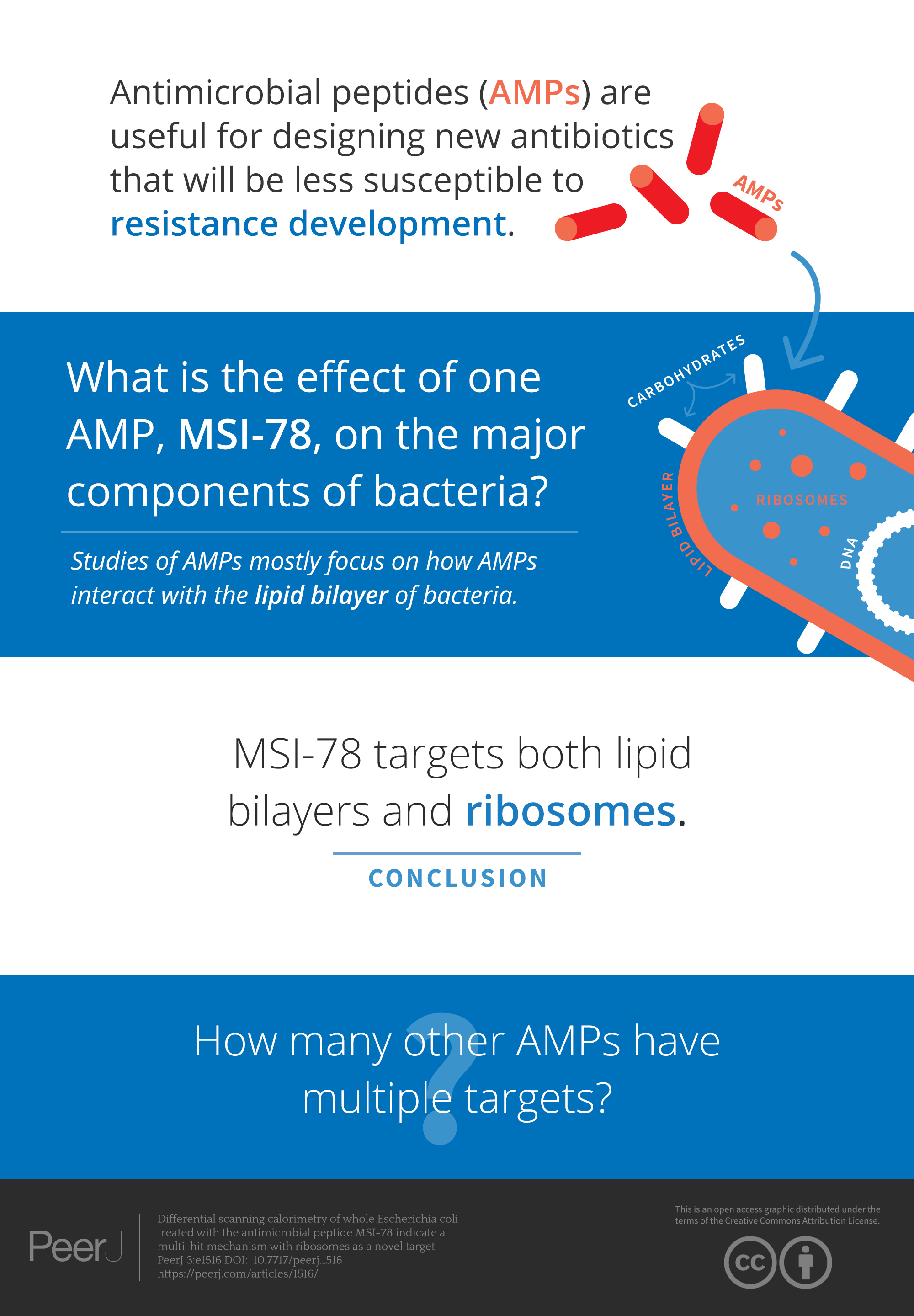
Anti – drug resistance molecules target both ribosomes & cell membrane
Differential scanning calorimetry of whole Escherichia coli treated with the antimicrobial peptide MSI-78 indicate a multi-hit mechanism with ribosomes as a novel target. Drug resistant infections are becoming a huge problem and antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), have been proposed to be useful for designing new antibiotics that will be less susceptible to resistance development. Most researchers focus on how AMPs interact with the lipid bilayer of bacteria. Using a technique (differential scanning calorimetry = DSC) to study the effect of one AMP (MSI-78) on all parts of the bacteria, researchers found MSI-78 doesn’t just target lipid bilayers - it messes up ribosomes as well.
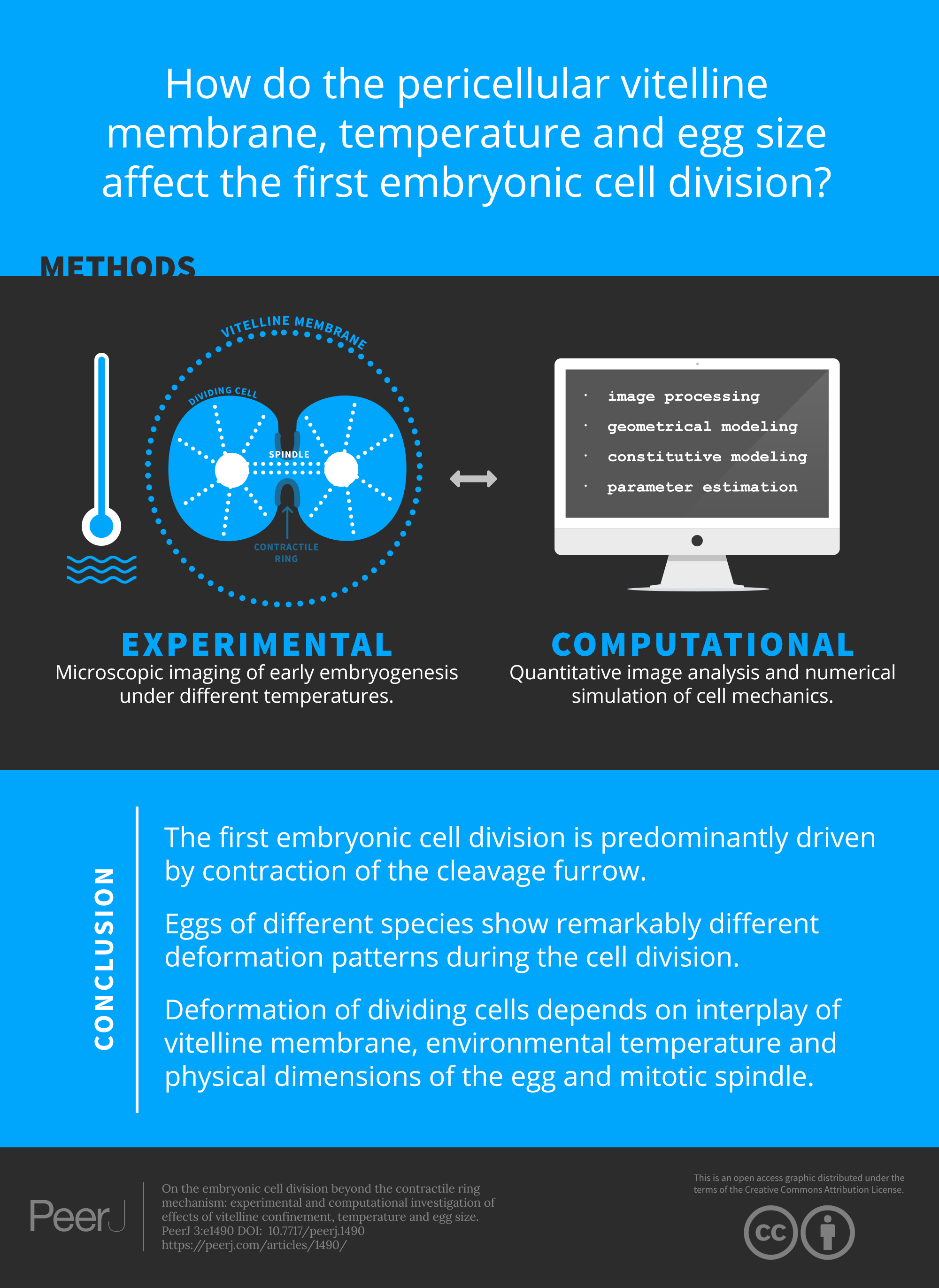
Embryonic cell division & the vitelline membrane
On the embryonic cell division beyond the contractile ring mechanism: experimental and computational investigation of effects of vitelline confinement, temperature and egg size. The first embryonic cell division is predominantly driven by contraction of the cleavage furrow. Eggs of different species show remarkably different deformation patterns during the cell division. Deformation of dividing cells depends on interplay of vitelline membrane, environmental temperature and physical dimensions of the egg and mitotic spindle.
Academic inequality: country reputation controls publishing
Academic inequality through the lens of community ecology: a meta-analysis. A synthesis based on ecological meta-analysis papers found that author diversity in terms of author affiliation has little increased and rather country reputation was more powerful than the popularity of the scientific topic and affected the chance of publication.
Cognitive factors influence self-reported vision
Trail Making Test performance contributes to subjective judgment of visual efficiency in older adults. When we provide a subjective judgment on our own vision (‘How would you rate your vision?') this judgement is determined by several factors, one very important is of course your visual acuity (ie. what you get at the ophthalmologist) but there are higher level factors that play a part. These higher level factors are for example how able you are to use the good or poor vision that you have in tasks with different demands. What we tried to do is use a quite basic visual task requiring cognitive input (Trail Making Test) and show that performance on this test predicts (to some extent) the answer to the How would you rate your vision question. We argue that this indicates that people are (somehow) considering this ‘higher level’ when judging their own vision.
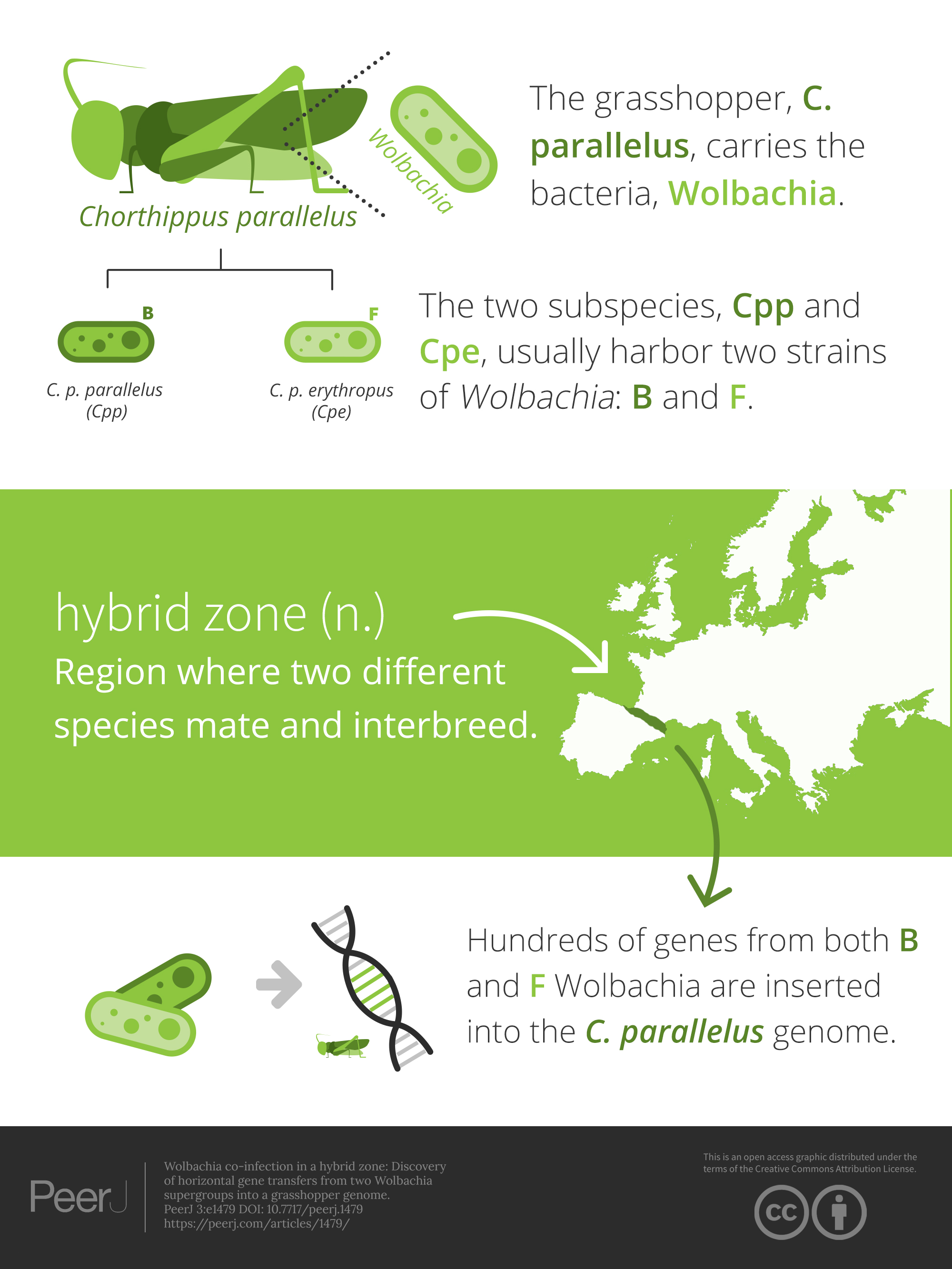
Interbreeding grasshoppers exchange bacterial genomes
Wolbachia co-infection in a hybrid zone: discovery of horizontal gene transfers from two Wolbachia supergroups into an animal genome. Two subspecies of Chorthippus parallelus grasshoppers (Cpp and Cpe) are infected with two different strains of a bacteria called Wolbachia. When Cpp and Cpe interbreed in a hybrid zone between France and Spain, the hybrid grasshoppers can acquire both types of Wolbachia. By studying the genomes of hybrid grasshoppers, researchers found that genes from both Wolbachia strains have moved from the bacterial genome into the grasshopper genome.