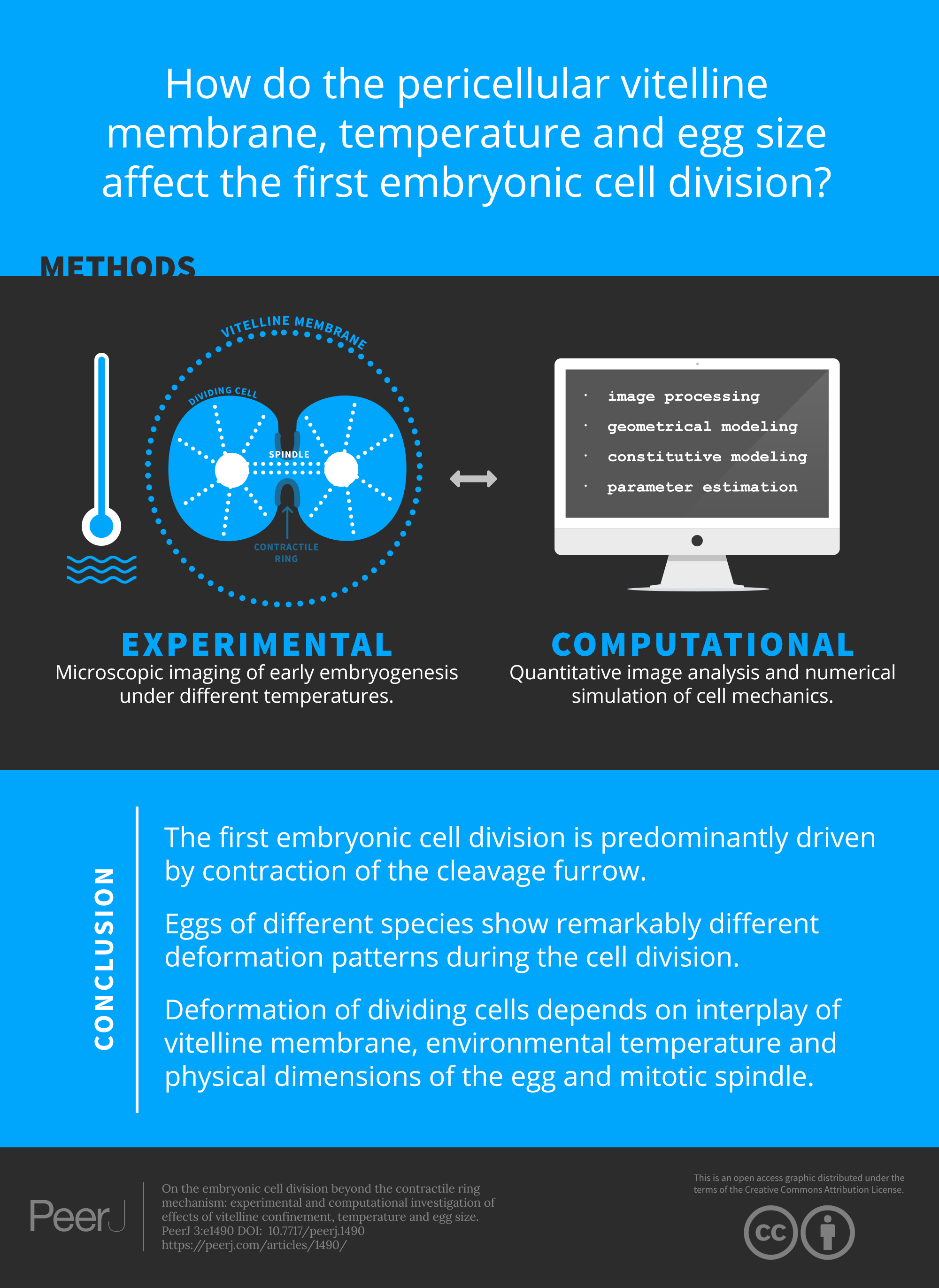
Embryonic cell division & the vitelline membrane
On the embryonic cell division beyond the contractile ring mechanism: experimental and computational investigation of effects of vitelline confinement, temperature and egg size. The first embryonic cell division is predominantly driven by contraction of the cleavage furrow. Eggs of different species show remarkably different deformation patterns during the cell division. Deformation of dividing cells depends on interplay of vitelline membrane, environmental temperature and physical dimensions of the egg and mitotic spindle.