LAY SUMMARY
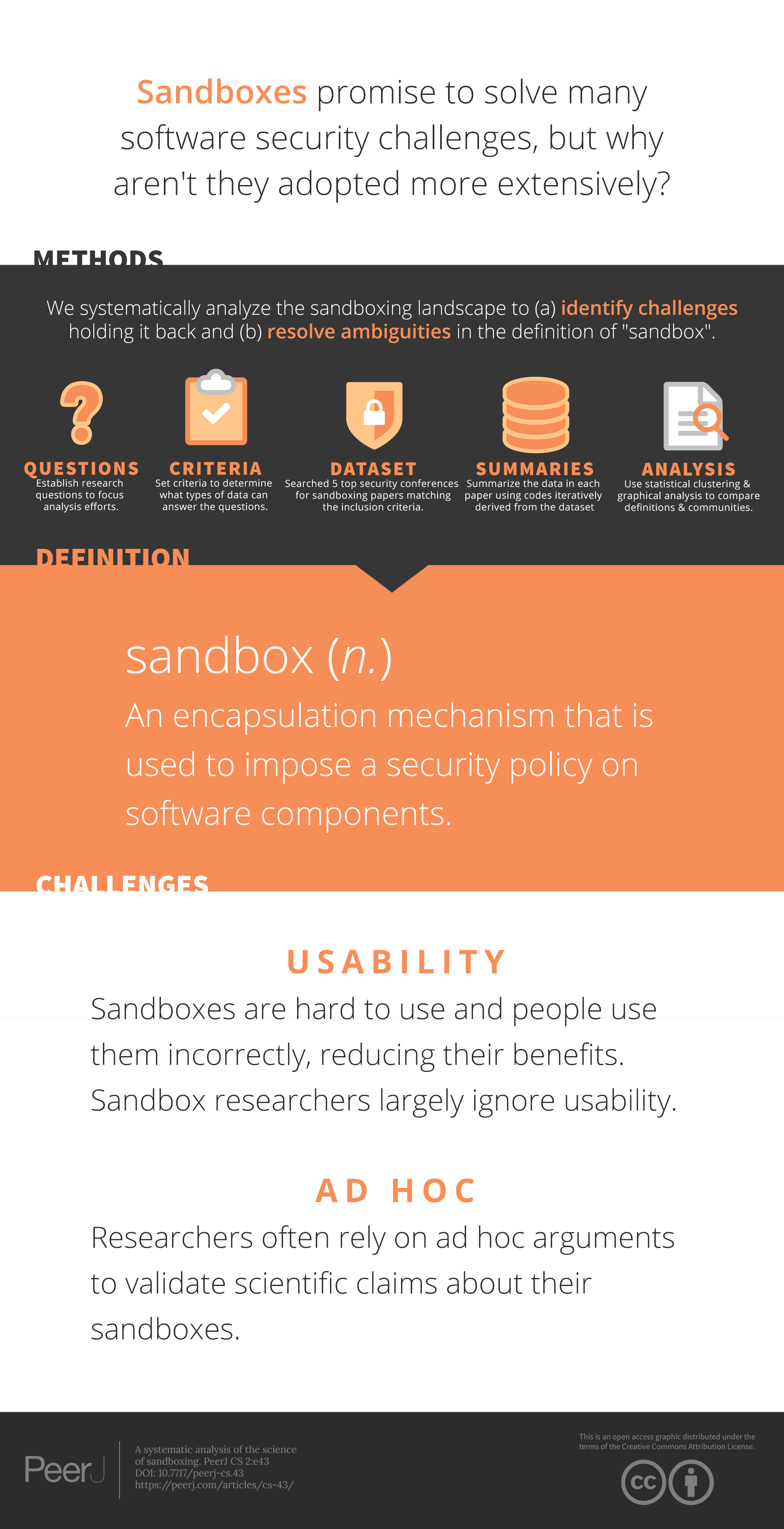
Sandboxing is a software security sub-discipline that doesn’t have a specific definition. By studying a large dataset of papers within the sandboxing discipline, researchers first established a definition for the term. However, the study also found areas for improvement within the discipline: (1) the arguments researchers present are often ad hoc and (2) sandbox usability is mostly uncharted territory. We propose ways to structure arguments to ensure they fully support their corresponding claims and suggest lightweight means of evaluating sandbox usability.
ABSTRACT
Sandboxes are increasingly important building materials for secure software systems. In recognition of their potential to improve the security posture of many systems at various points in the development lifecycle, researchers have spent the last several decades developing, improving, and evaluating sandboxing techniques. What has been done in this space? Where are the barriers to advancement? What are the gaps in these efforts? We systematically analyze a decade of sandbox research from five top-tier security and systems conferences using qualitative content analysis, statistical clustering, and graph-based metrics to answer these questions and more. We find that the term “sandbox” currently has no widely accepted or acceptable definition. We use our broad scope to propose the first concise and comprehensive definition for “sandbox” that consistently encompasses research sandboxes. We learn that the sandboxing landscape covers a range of deployment options and policy enforcement techniques collectively capable of defending diverse sets of components while mitigating a wide range of vulnerabilities. Researchers consistently make security, performance, and applicability claims about their sandboxes and tend to narrowly define the claims to ensure they can be evaluated. Those claims are validated using multi-faceted strategies spanning proof, analytical analysis, benchmark suites, case studies, and argumentation. However, we find two cases for improvement: (1) the arguments researchers present are often ad hoc and (2) sandbox usability is mostly uncharted territory. We propose ways to structure arguments to ensure they fully support their corresponding claims and suggest lightweight means of evaluating sandbox usability.
CITATION
(2016) A systematic analysis of the science of sandboxing. PeerJ Computer Science 2:e43 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.43